Osmoregulation: The Essential Process for Maintaining Internal Balance
.
Editor's Notes: Osmoregulation: The Essential Process for Maintaining Internal Balance have published today date. Given its importance, we put together this guide to help target audience make the right decision.
Osmoregulation refers to the active regulation of the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids to maintain the homeostasis of the body's internal environment and cells. It involves controlling the balance of water and solutes (such as salts and ions) within the body, ensuring that cells function optimally. Osmoregulation is crucial for all living organisms, from simple cells to complex multicellular organisms, as it helps maintain the stability of their internal environment and allows them to adapt to changing external conditions.
| Osmoregulation | Thermoregulation |
|---|---|
|
It involves regulating the osmotic pressure of an organism's body fluids. It is a process that helps maintain the balance of water and solutes within the body. It allows organisms to adapt to changing external conditions and maintain the stability of their internal environment. |
It ensures the body remains at an optimal temperature range. It is crucial for maintaining internal body temperature within specific limits. It helps organisms withstand fluctuations in the external environment and maintain homeostasis. |
| e.g Freshwater organisms, such as fish and amphibians, have evolved specialized mechanisms to excrete excess water and retain solutes | e.g Mammals and birds utilize mechanisms such as sweating, panting, and shivering to regulate body temperature |
FAQ
Osmoregulation is a crucial biological process that ensures the stability of internal environments in living organisms. By regulating the balance of water and solutes, it maintains optimal conditions for cellular function and overall health. However, various misconceptions and uncertainties surround this essential process. This FAQ section aims to address common concerns and provide accurate information based on scientific research. Osmoregulation: The Essential Process For Maintaining Internal Balance

Chap 48-Osmoregulation SM16 - Chapter 47: Osmoregulation Maintaining - Source www.studocu.com
Question 1: What is the primary function of osmoregulation?
Answer: The primary function of osmoregulation is to maintain a stable internal environment for cells and tissues by regulating the balance of water and solutes, such as ions and organic molecules. This process ensures optimal conditions for cellular activities, including metabolism, protein synthesis, and waste removal.
Question 2: How do different organisms achieve osmoregulation?
Answer: Organisms have evolved diverse mechanisms for osmoregulation depending on their habitat and physiological requirements. Marine organisms, for instance, possess specialized structures like salt glands to excrete excess ions and maintain proper water balance. Freshwater organisms, on the other hand, have adaptations to prevent excessive water uptake and maintain solute concentrations.
Question 3: What are the potential consequences of osmoregulatory failure?
Answer: Osmoregulatory failure can lead to severe physiological consequences. Dehydration, resulting from inadequate water retention, can disrupt cellular functions and ultimately lead to organ dysfunction and cell death. Conversely, overhydration, caused by excessive water intake, can cause cell swelling and electrolyte imbalances, potentially leading to neurological complications.
Question 4: How does osmoregulation contribute to overall health and well-being?
Answer: Osmoregulation plays a pivotal role in maintaining overall health and well-being by ensuring the proper functioning of cells and tissues. It regulates blood pressure, nerve impulses, and body temperature. A balanced internal environment supports optimal immune function, cognitive performance, and physical endurance.
Question 5: Can external factors influence osmoregulation?
Answer: Yes, external factors can indeed influence osmoregulation. Environmental changes, such as temperature fluctuations or extremes in water availability, can impact the ability of organisms to maintain internal balance. Certain medications or medical conditions can also affect osmoregulatory mechanisms.
Question 6: What are some common misconceptions about osmoregulation?
Answer: One common misconception is that only aquatic organisms require osmoregulation. However, all living organisms, including terrestrial species, have evolved osmoregulatory mechanisms to maintain internal stability. Another misconception is that osmoregulation is solely about maintaining water balance. In reality, it also involves regulating solute concentrations, such as ions and organic molecules, to ensure optimal cellular function.
Osmoregulation is a fascinating and complex biological process that plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and well-being of all living organisms. By understanding the principles and mechanisms of osmoregulation, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable adaptations that have evolved to sustain life in diverse environments.
Tips for Effective Osmoregulation
Osmoregulation, the process of maintaining a stable internal environment despite external fluctuations, is crucial for overall health and well-being. Here are some tips to optimize osmoregulation processes:
Tip 1: Maintain Adequate Hydration
Water is essential for osmoregulation, as it helps transport ions and nutrients throughout the body. Aim to consume eight to ten glasses of water per day, more if engaged in strenuous activities.
Tip 2: Monitor Electrolyte Intake
Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and chloride, play a vital role in osmoregulation. Monitor your electrolyte intake, especially if you exercise vigorously or sweat excessively. Sports drinks can provide electrolytes, or consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Tip 3: Avoid Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol inhibits the production of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which helps the kidneys conserve water. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to dehydration and disrupt osmoregulation.
Tip 4: Manage Caffeine Intake
Caffeine is a diuretic that increases urine production and can contribute to dehydration. Limit caffeine intake to maintain optimal hydration levels.
Tip 5: Monitor Blood Pressure
Osmoregulation can affect blood pressure. Regularly monitor your blood pressure to ensure it is within a healthy range. If you have high blood pressure, consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
By following these tips, you can support effective osmoregulation, maintain internal balance, and promote overall health and well-being.
Osmoregulation: The Essential Process For Maintaining Internal Balance
Osmoregulation, the regulation of solute and water balance, is a fundamental physiological process necessary for maintaining homeostasis in living organisms. It ensures that internal body fluids remain within a specific range, despite constant external fluctuations in solute concentration and water availability. This process involves various essential aspects, each playing a crucial role in safeguarding the integrity and proper functioning of biological systems.
- Water and Ion Transport: Regulating the movement of water and ions across cell membranes to maintain proper hydration and electrolyte balance.
- Hormonal Control: Hormones, such as antidiuretic hormone and aldosterone, play a vital role in regulating osmoregulation by influencing water and ion reabsorption in the kidneys and other organs.
- Osmoreceptors: Specialized cells that detect changes in osmotic pressure, triggering appropriate physiological responses to maintain internal balance.
- Excretion and Reabsorption: The kidneys play a crucial role in osmoregulation by excreting excess solutes and reabsorbing water, maintaining the proper balance of fluids and electrolytes.
- Osmoregulation in Different Environments: Organisms have evolved various adaptations to maintain osmotic balance in different environments, such as marine, freshwater, and desert habitats.
- Pathophysiological Significance: Disturbances in osmoregulation can lead to various pathophysiological conditions, such as dehydration, water intoxication, and electrolyte imbalances.
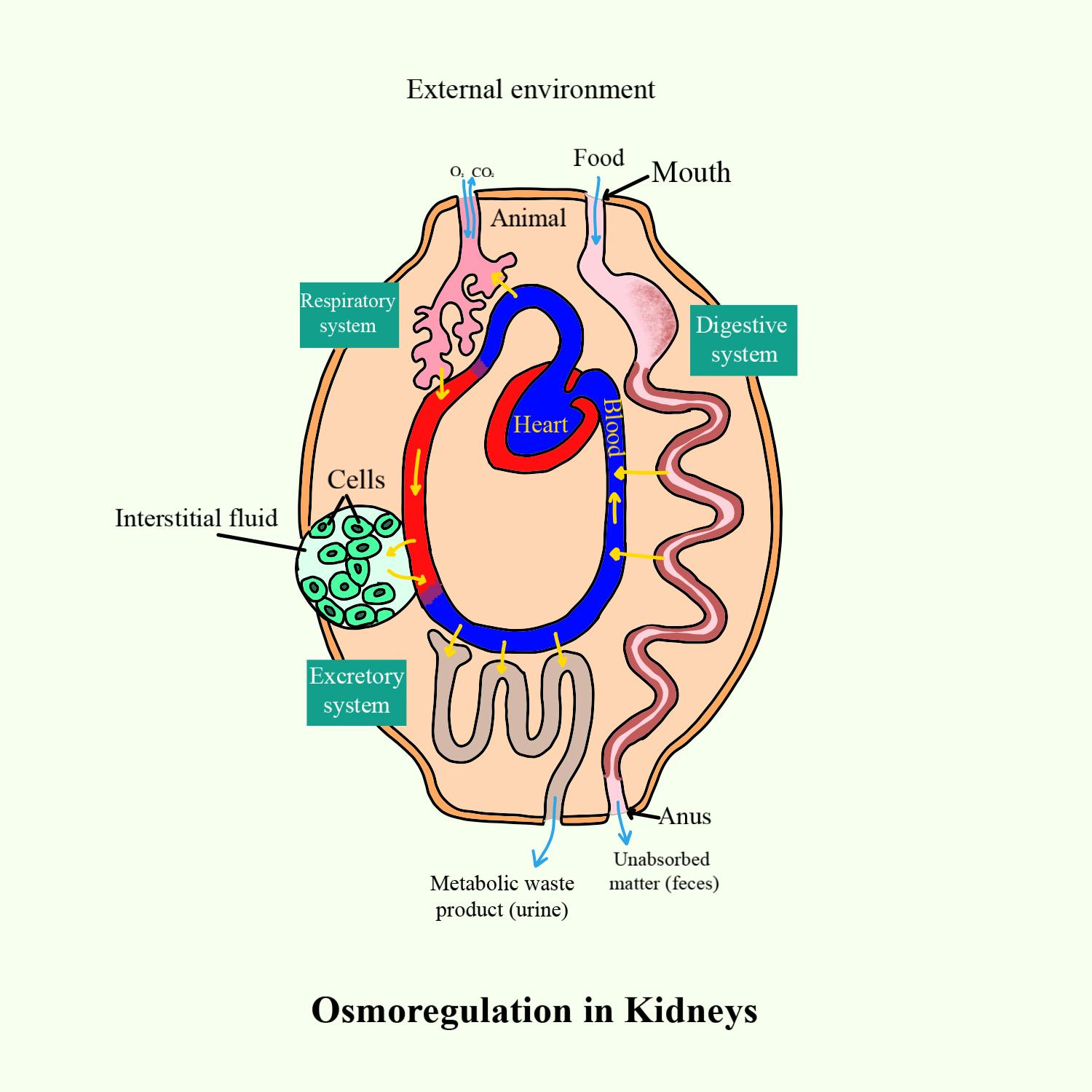
Describe how the kidneys help in osmoregulation in humans. - Source www.vedantu.com
Osmoregulation is a complex and interconnected process involving various physiological mechanisms to maintain internal balance. Understanding these aspects provides valuable insights into the delicate interplay between osmoregulation and an organism's ability to survive and thrive in diverse environments.
Osmoregulation: The Essential Process For Maintaining Internal Balance
Osmoregulation is the process by which organisms regulate the balance of water and dissolved substances (solutes) in their bodies. It is essential for life, as cells can only function properly within a narrow range of osmotic pressure. If the osmotic pressure of the cell's surroundings is too high, water will leave the cell, causing it to shrink and die. Conversely, if the osmotic pressure of the cell's surroundings is too low, water will enter the cell, causing it to swell and burst.

Osmoregulation-QUIZ - quiz - OSMOREGULATION QUIZ (group 5) What is - Source www.studocu.com
Osmoregulation is carried out by a variety of mechanisms, including the active transport of ions and the synthesis of organic solutes. The kidneys play a particularly important role in osmoregulation, as they are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine. The concentration of urine can be varied to either conserve water or excrete excess water, depending on the needs of the body.
Osmoregulation is essential for all living organisms, from single-celled bacteria to multicellular animals. It is a complex process that involves a variety of mechanisms, and it is essential for maintaining the internal balance of water and dissolved substances that is necessary for life.
Table: Examples of Osmoregulation in Different Organisms
| Organism | Osmoregulatory Mechanism |
|---|---|
| Bacteria | Active transport of ions |
| Plants | Synthesis of organic solutes |
| Mammals | Kidneys |
Conclusion
Osmoregulation is a vital process that allows organisms to maintain the internal balance of water and dissolved substances that is necessary for life. It is carried out by a variety of mechanisms, including the active transport of ions, the synthesis of organic solutes, and the excretion of urine. Osmoregulation is essential for all living organisms, and it plays a key role in maintaining the homeostasis of the body.
Despite the challenges posed by environmental changes, osmoregulation remains a fundamental process that allows organisms to survive and thrive. Understanding the mechanisms of osmoregulation is therefore essential for the advancement of biology and medicine.
